转自“中关村NMT联盟”

期刊:BMC Plant Biology
主题:油菜素内酯促黄瓜根系铵硝吸收机制
标题:24-Epibrassinolide promotes NO3- andNH4+ ion flux rate and NRT1 gene expression in cucumber under suboptimal root zone temperature
影响因子:3.930
检测指标:NO3-、NH4+流速
检测部位:根毛区
作者:中国农业科学院蔬菜与花卉研究所Ali Anwar、李衍素、于贤昌
英文摘要
Suboptimal root zone temperature (RZT) causes a remarkable reduction in growth of horticultural crops during winter cultivation under greenhouse production. However, limited information is available on the effects of suboptimal RZT on nitrogen (N) metabolism in cucumber seedlings. The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of 24-Epibrassinolide (EBR) on nitrate and ammonium flux rate, N metabolism, and transcript levels of NRT1 family genes under suboptimal RZT in cucumber seedlings.
Suboptimal RZT (LT) negatively affected on cucumber growth and proportionately decreased EBR contents, bleeding rate, root activity, enzyme activities of nitrate reductase (NR), nitrite reductase (NiR), glutamine synthetase (GS), and glutamate synthase (GOGAT), nitrate (NO3−) influx rate, ammonium (NH4+) efflux rate, and transcript levels of nitrate transporter (NRT1) encoding genes. However, exogenous EBR reduced the harmful effects of suboptimal RZT and increased endogenous EBR contents, bleeding rate, root activity, enzyme activities of NR, NiR, GS, and GOGAT, NH4+ and NO3− flux rates and contents, and N accumulation. EBR-treated seedlings also upregulated the transcript levels of nitrate transporters CsNRT1.1, CsNRT1.2A, CsNRT1.2B, CsNRT1.2C, CsNRT1.3, CsNRT1.4A, CsNRT1.5B, CsNRT1.5C, CsNRT1.9, and CsNRT1.10, and downregulated CsNRT1.5A and CsNRT1.8. LT treatment upregulated the expression level of CsNRT1.5A, while exogenous BZR application downregulated the expression level of NRT1 genes.
These results indicate that exogenous application of EBR alleviated the harmful effects of suboptimal RZT through changes in N metabolism, NH4+ and NO3− flux rates, and NRT1 gene expression, leading to improved cucumber seedlings growth. Our study provides the first evidence of the role of EBR in the response to suboptimal RZT in cucumber, and can be used to improve vegetable production.
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
次优根区温度(RZT)导致在温室生产期间冬季栽培期间园艺作物的生长显着减少。然而,关于次优RZT对黄瓜幼苗中氮(N)代谢的影响的信息有限。本研究的目的是研究24-表油菜素内酯(EBR)对黄瓜幼苗次优RZT下NRT1家族基因的**盐和铵通量,N代谢和转录水平的影响。
次优RZT(LT)对黄瓜生长有负面影响,并且比例降低EBR含量,出血率,根系活力,**还原酶(NR),亚**还原酶(NiR),谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)和谷氨酸合成酶(GOGAT)的酶活性,**盐(NO3-)流入速率,铵(NH4 +)流出速率和**盐转运蛋白(NRT1)编码基因的转录水平。然而,外源EBR降低了次优RZT的有害作用,增加了内源EBR含量,出血率,根系活力,NR,NiR,GS和GOGAT的酶活性,NH4 +和NO3-通量率和含量以及N积累。 EBR处理的幼苗也上调了**盐转运蛋白CsNRT1.1,CsNRT1.2A,CsNRT1.2B,CsNRT1.2C,CsNRT1.3,CsNRT1.4A,CsNRT1.5B,CsNRT1.5C,CsNRT1.9和CsNRT1的转录水平。 .10,并下调CsNRT1.5A和CsNRT1.8。 LT处理上调CsNRT1.5A的表达水平,而外源BZR应用下调NRT1基因的表达水平。
这些结果表明,外源施用EBR通过改变N代谢,NH4 +和NO3-通量率以及NRT1基因表达减轻了次优RZT的有害作用,从而改善了黄瓜幼苗的生长。我们的研究首次证明了EBR在黄瓜中对次优RZT的反应中的作用,并可用于改善蔬菜生产。
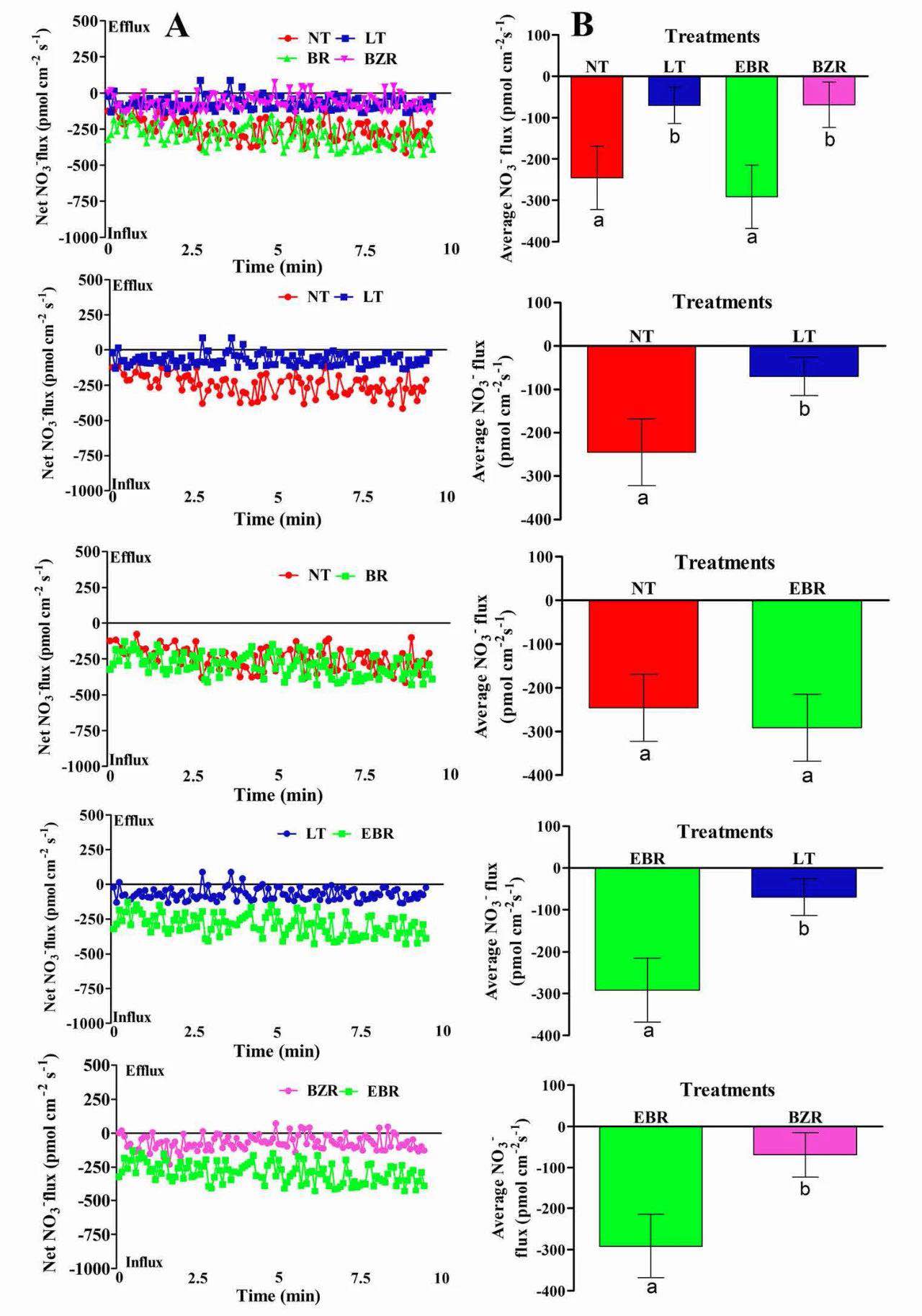
Fig. 4 Effects of suboptimal RZT and EBR on NO3- (A; scatter NO3- flux rate, B; average NO3- flux rate) flux rate in roots of cucumber seedlings under suboptimal RZT treatment. Flux rate was recorded for 10 min in roots seven days after treatment. Each point is the mean of nine individual seedlings and bars indicate standard deviations. Treatments with the same letters are not significantly different by the least significant difference (LSD) test at P = 0.05
文章链接:
https://bmcplantbiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12870-019-1838-3
中关村NMT联盟统筹安排全国NMT测试服务,如需开展NMT相关实验,请联系联盟:010-8262 4800转12
旭月版权所有,转载注明出处
